Canonical URLs help webmasters solve the problem of duplicate content issues.
Knowing how to implement them correctly is essential for SEO.
Besides, using them inaccurately can adversely affect your site's performance.
Canonical tags have been around since 2009. Google, Microsoft, and Yahoo united to create them to help site owners quickly solve duplicate content issues.
This article will discuss what canonical URLs are, how they work, why they are crucial for your website, and how to use them.
Let's begin!
What is a Canonical URL?
Canonical URL, aka canonical tag, is an HTML link element with the attribute of rel=canonical found in the <head> element of your webpage.
Canonical tags tell search engines the preferred URL from among different web page versions.
The search engines know which webpage to crawl and index with the help of canonical tags. This is critical because URLs can have variations yet similar content.
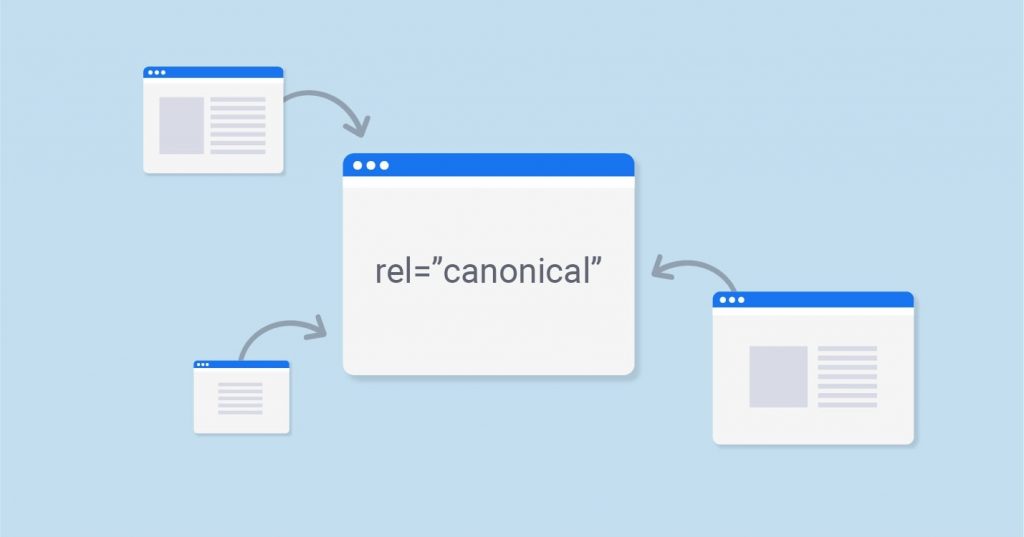
Image source: Digital Garg
Compare the following URLs:
- www.example.com
- https://m.example.com
- https://amp.example.com
- https://example.com?ref=twitter
Although the URLs are different, they refer to the same webpage.
Search engines can find this challenging because they might not know which one has the right content.
However, if you use a canonical URL, search engines will rank only the preferred version of your URL from a set of URLs and ignore the rest.
Hence, even though different URLs on the site have the same content, your site won't get penalized by Google.
Why Do I have Duplicate Content?
If you own a website, you know that content is king. Besides bringing and engaging visitors to your site, it's what search engines analyze when ranking websites.
If your content is unique, relevant, and engaging, it has a higher chance of ranking higher in the search engines.
On the contrary, search engines will decrease your ranking if your site has duplicate content.
Some webmasters don't even know they have duplicate content on their websites.
So, what are the reasons for duplicate content?
Various reasons can lead to content duplication. These include:
- Regional domain prefix: If your website is available in different regions, you need to use canonical tags to point to the main content to prevent duplicate content.
- Transfer protocol/subdomain variations: If you can access a site through different URLs, as shown earlier, search engines will consider these as separate pages.
- Mobile versions: Mobile site versions are often available through different URLs. You need to use canonical tags to differentiate the two.
- Product pages: The issue of duplicate content is rampant in eCommerce stores, especially when there are different variations of the same product.
- Copied content: You may need more than one website to publish the same content in some cases. If this is the case, you should canonicalize the preferred content.
Image source: Explore Insiders
Google Panda was an algorithm launched in 2011 that penalized sites having lots of duplicates and low-quality content. Now, Panda is a part of Google's core algorithm.
If you don't want Panda to hit your site, you should identify and fix duplicate content issues on your site with the help of canonical URLs.
What Does a Canonical Tag Look Like?
Here is how a canonical URL looks like:
<link rel="canonical” href="https://example.com">
Suppose you have an eCommerce product page - myecommercesite.com/product-a
Now, this product can be accessed from a number of URLs such as:
myecommercesite.com/allproducts/product-a
myecommercesite.com/top-selling-products/product-a
myecommercesite.com/products-priced-below-100/product-a
There can be many different URLs that might point to the same content.
In such a case, you should add a canonical URL in the head section of all the duplicate pages to tell search engines the correct version of the URL.
In our example, we want to keep the URL: myecommercesite.com/product-a as the preferred URL. So, we will add the following canonical tag in the <head> section of all the three duplicate content pages:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://myecommercesite.com/product-a"/>
Why Are Canonical Tags/URLs Important For SEO?
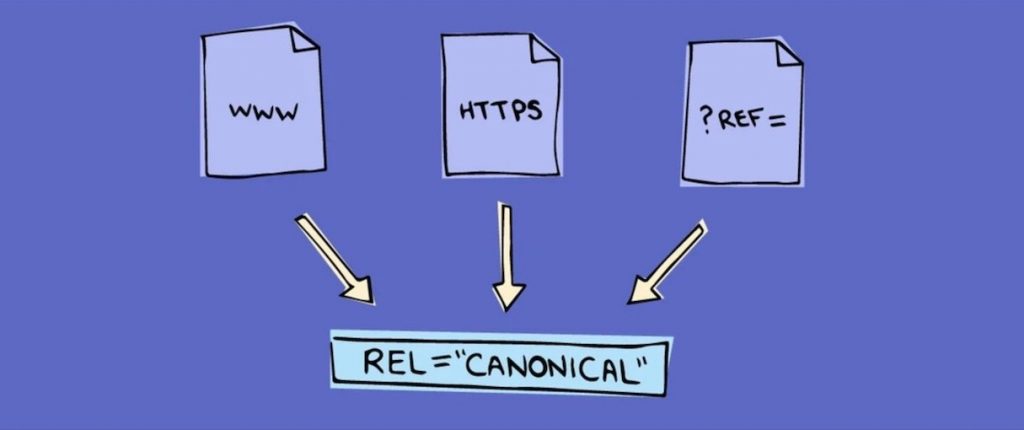
Image source: Shopify
The primary function of canonical tags is to solve duplicate content issues.
However, canonical URLs are also crucial for SEO. Here’s why.
Canonical Tags Specify the URL That You Want to Be Displayed in Search Results
When you set a canonical tag, search engines know which version of the page to display. Duplicate content can cause several SEO problems, and search engines might not know which content to rank. As such, they miss some of your authoritative content.
Canonical Tags Simplify Tracking Metrics for a Single Product/Topic
When there are several URLs, it can be challenging to get consolidated metrics for individual content. However, using canonical tags makes it easier to track the performance of each page.
It Prevents Googlebot from Crawling Duplicate Pages
If you have a large website, canonical tags ensure Googlebot crawls your new webpages instead of the duplicated versions of the same content. However, this can only be an issue if you have hundreds or thousands of pages.
Canonical URLs Consolidate Links for Duplicate Content and Manage Syndicated Content
Canonical URLs help search engines combine information about a URL into one authoritative URL. Besides, they also help to consolidate page ranking to your preferred URL.
When and How Should You Use Canonical Tags?
Now that you understand what canonical tags are and their importance to SEO let’s see when and how to use them.
- Use canonical tags whenever you have duplicate content on your site.
- Use them when offering similar products with a slight difference, especially if you own an eCommerce store.
- Use them when structuring additional information for a specific URL. It sorts and specifies content on a webpage (URL parameters).
Difference Between Canonical Tags and 301 Redirects
Many people use canonical tags, and 301 directs interchangeably.
However, they are different from each other.
Canonical tags help you specify the URL you want to be displayed in Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs).
On the contrary, a 301 redirect helps permanently move one URL to another. When a user types in a URL, it redirects them to another URL. It communicates to servers, browsers, and users that the URL they are trying to access has been moved to another URL. Users don’t notice 301 redirects because the final URL loads in the browser.
Here’s when to use 301 redirects:
- When there is a change in the domain name due to rebranding.
- If you’ve changed the URLs of your website.
- When a page from your website no longer exists.
How to Create Canonical Tags on WordPress
The easiest way to create and use canonical tags on WordPress is to download a WordPress plugin such as Yoast SEO or RankMath.

Here are the steps to create canonical URLs using Yoast SEO:
- Log in to your WordPress site.
- Navigate to the page or post that you want to change.
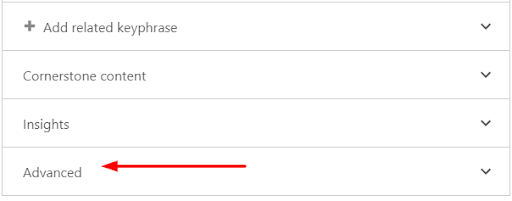
- Head over to the advanced section of the Yoast SEO meta box under the ‘SEO’ tab.
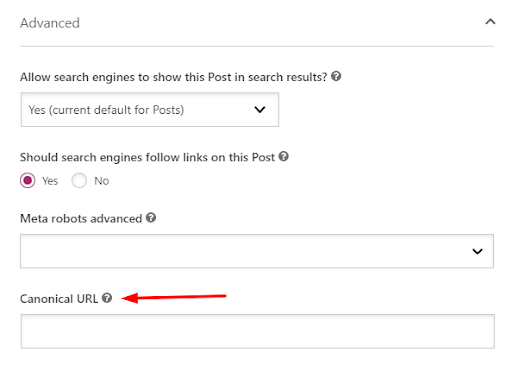
- Enter the complete canonical tag, including http/s and www or non-www, in the ‘Canonical URL’ field.
- Update the post/ page
If you’re using the RankMath SEO plugin, follow the below steps to create canonical URLs:
- Edit the post/page. Go to the specific article you want to canonicalize and click on ‘Edit.’
- Navigate to the advanced tab located in the Dashboard.
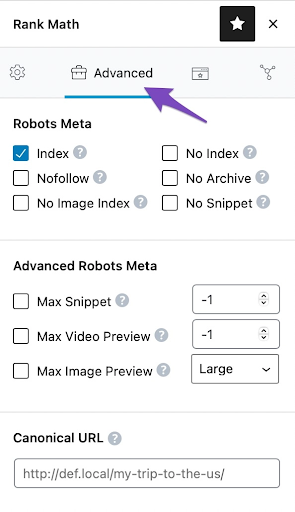
Source: Rankmath
- Change the canonical URL field to point to the main source of your content.
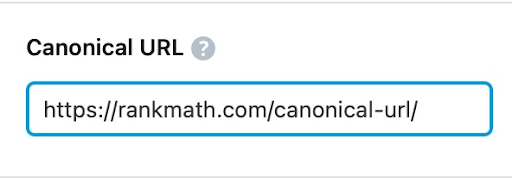
Source: Rankmath
Once you’ve set the canonical tag, save the post and update just as you do after publishing a post.
How to Create Canonical Tags in Wix
Wix automatically generates canonical tags for all your posts.
Here’s how to change a custom canonical tag in Wix:
- Click on the current page in the top left corner and scroll down to manage pages within the site editor.
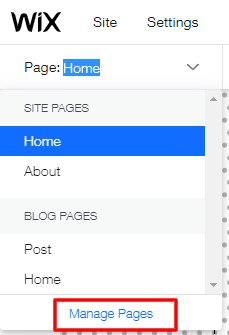
- A list of pages will show up. Click SEO basics.
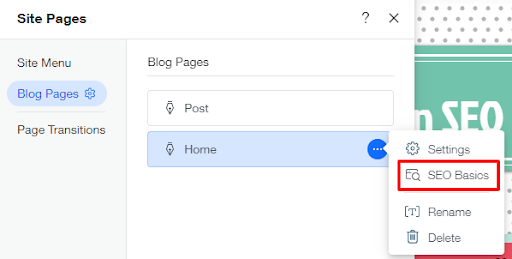
- Click on the ‘Advanced SEO’ tab and scroll down to find the canonical URL field, and click ‘Edit.’
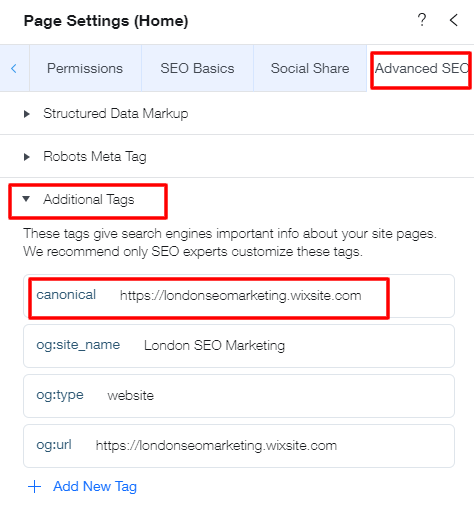
- Edit your tag under ‘Tag value.’
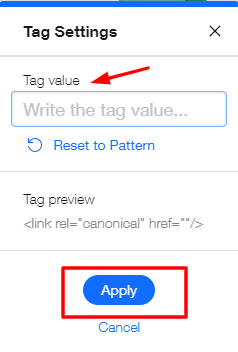
- Click ‘Apply.’
You can also remove a canonical tag and restore the original one. Here’s how to do it:
- Go to your page’s SEO settings
- Head over to the ‘Advanced SEO’ tab.
- Hover over the tag over Meta Tags.
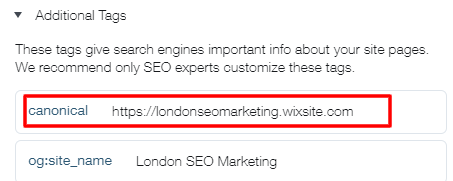
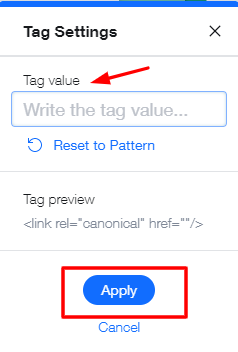
- Click the ‘Show more icon.’
- Click ‘Edit.’
- Click ‘Reset Pattern.’
How to Create Canonical Tags in Shopify
One of the major problems you can face when using Shopify is product duplication. This can limit your ranking ability.
However, you can reduce product duplication issues by the use of accurate canonical tags.
You need to edit how your site generates or pulls its canonical tags.
Here’s how to do it:
To add a canonical tag in the Shopify store, add your store’s theme and select “Edit code” under “Actions.”
Now, locate theme.liquid that you can find under “Layout.” Here, you need to enter the below code above </head> closing.
<link rel="canonical" href="{{ canonical_url }}"/>
- Click the ‘Show more icon.’
- Click ‘Edit.’
- Click ‘Reset Pattern.’
Canonical Tag Best Practices
Keep the following best practices in mind when optimizing canonical URLs:
Use Absolute URL
You can use rel=” canonical ” with absolute or relative links. However, to minimize confusion, you should always use absolute URLs, such as:
<link rel=” canonical” href= “https://www.website.com/page-a/”/>
And not:
<link rel=” canonical” href=”/page-a/”/>
Audit Your Site for Canonicalization Issues
Always inspect your web pages to ensure duplicate content has a canonical tag. To inspect any URL, you can simply check the HTML source code of any page to determine if a canonical tag has been added to any duplicate pages.
You need to ensure that the page is crawlable and indexable. Open Search Console and enter the page URL at the top of the bar, as shown in the image below.
Now, wait for some second, and the tool will tell you whether your page is crawlable and indexable or not.
Use Canonical Tags Sparingly
You should only canonicalize pages that have duplicate content; otherwise, you risk excluding other relevant pages from rankings. So, only canonicalize if the pages are similar.
Canonicalize Your Homepage
It's always recommended to canonicalize your homepage because it's your most referenced page. Besides, homepage duplicates are the most common.
Always Use Lowercase URLs
Search engines treat uppercase and lowercase URLs as different URLs. When using canonical tags, use the lower case for consistency. This is important because it ensures the right URL is indexed.
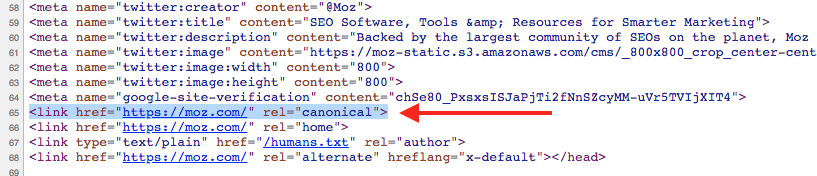
Use The Correct Domain Version
HTTP and HTTPS are not interchangeable, and if you interchange their canonical tags, it could confuse the search engine bots. So, if your site uses HTTP, don’t set your canonical tags with HTTPS.
However, Google recommends using HTTPS on your site to improve user experience. Hence, you should move your site from HTTP to HTTPS to make it secure and UX-friendly.
Mistakes to Avoid When Implementing Canonical Tags
Implementing canonical tags can be tricky. Here are mistakes to avoid when implementing canonical tags.
Do Not Block Google from Crawling Specific URLs Via Robots.txt
If Google does not crawl or index a page, the page won’t have any chances of ranking. Instead of blocking Googlebot from crawling different pages, use canonical links, and the search engines will themselves know which page to display.
Mixed Signals
Only canonicalize one source of original content for multiple pages. In simple terms, don’t canonicalize page A > page B, and then page B > page A.
This is confusing, right? The search engine may make a bad choice. If page A is canonical, the correct canonicalizations scheme should be page B > page A; page C > page A; page D> A, and so forth.
Canonicalizing to a 301 Redirect
You should not canonicalize a URL that will be redirected. Instead, set the canonical link to be the redirect target.
Canonicalizing to Irrelevant Content
It’s easy to think canonicalizing unrelated content can increase page rank, but canonicalization doesn’t work this way—only canonical duplicate content.
Setting Multiple Canonical URLs
If you set multiple tags, they’ll be ignored by search engines. Don’t include two canonical tags within the <head>. If you set multiple tags, search engines will ignore them. So, each page should use a single canonical tag.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, a canonical tag is a URL chosen as the master URL for a set of duplicate web pages.
The biggest advantage of using canonical links is that it boosts SEO, increases traffic flow, and improves the reliability of data collected from Google Analytics.
Start using canonical URLs to upgrade your SEO strategy and bookmark this canonical tag guide for future reference.